
lex-o-pedia
Investigative Journalism or Privacy Invasion? Legal Analysis of Sting Operations in India
Sting operations are key investigative tools that expose corruption but often clash with privacy rights. Balancing freedom of the press with ethical limits raises significant legal and moral questions in India.

lex-o-pedia
Investigative Journalism or Privacy Invasion? Legal Analysis of Sting Operations in India
Sting operations are key investigative tools that expose corruption but often clash with privacy rights. Balancing freedom of the press with ethical limits raises significant legal and moral questions in India.

lex-o-pedia
What are the stages of crime under criminal law?
The stages of crime—intention, preparation, attempt, and commission—help determine criminal liability under Indian law, assessing the progression from thought to action for appropriate legal consequences.

lex-o-pedia
What is Waqf Under Muslim Law?
Wakf is the permanent dedication of property for religious or charitable purposes under Muslim law, either by will or during the dedicator's life, and governed by statutory provisions.

lex-o-pedia
What is the process for listing securities?
Listing securities involves registering financial instruments on a stock exchange, ensuring transparency and access to capital. Companies must meet regulatory requirements for investor protection.

lex-o-pedia
What is Law of Guardianship under Muslim law?
Under Muslim law, guardianship (Wilayat) includes managing a minor's personal and property interests. Types include natural, testamentary, court-appointed, and de-facto guardians, prioritizing the child's welfare.

lex-o-pedia
How do Hart and Fuller’s theories intersect in the analysis of law and morality?
Hart’s positivism argues that law is valid through procedural origins, independent of morality. Fuller’s natural law contends that ethical principles are essential to law’s legitimacy and social respect.

lex-o-pedia
What is Law of Maintenance under Muslim Law?
Muslim law mandates maintenance for dependents lacking self-support, prioritizing a wife's right over other relatives. Post-divorce, a fair provision is owed to a wife beyond the iddat, as upheld by Shah Bano's case.

lex-o-pedia
How does a comparative analysis of transfers by ostensible ownership differ from those by an unauthorized person who subsequently acquires interest?
Sections 41 and 43 of the Transfer of Property Act, 1882, protect transferees in good faith, focusing on ostensible ownership and unauthorized transfers, respectively, emphasizing reasonable care and representation.

lex-o-pedia
What are different forms of Government?
Governments shape society by how they distribute power and uphold citizen rights. This piece explores democracy, monarchy, authoritarianism, totalitarianism, and theocracy, examining their structures and impacts.

lex-o-pedia
What is Mubarat Divorce?
Mubara’at is a form of Islamic divorce where both spouses mutually agree to end their marriage due to mutual dissatisfaction. Unlike Khula, it is initiated by either party and requires no compensation.

lex-o-pedia
Regulation of combinations under the Competition Act, 2002: Balancing growth and fair competition
The Competition Act, 2002 regulates mergers and acquisitions to prevent monopolies, fostering market fairness. The CCI balances growth with competition, ensuring consumer welfare and economic efficiency.

lex-o-pedia
Regulatory Framework Relating to Books of Accounts of a Company under the Companies Act, 2013
Under the Companies Act, 2013, companies must maintain detailed books of accounts, either physically or electronically, to ensure transparency and accountability. Directors and CFOs hold responsibility for compliance.

lex-o-pedia
The Principle of Competence-Competence & the Jurisdiction of Arbitral Tribunals
The Kompetenz-Kompetenz principle grants arbitral tribunals authority to determine their own jurisdiction, including challenges to the validity of the arbitration agreement, minimizing court intervention.

lex-o-pedia
Are Government Companies considered a ‘State’ under Constitutional Law?
Government companies, often termed as "State" under Article 12 of the Indian Constitution, are subject to judicial review based on government control, public function, and alignment with state interests.

lex-o-pedia
What is the Concept and Process of Appeal in the Code of Civil Procedure (CPC)?
Appeals in the Indian Code of Civil Procedure enable dissatisfied parties to seek higher court review of lower court judgments, ensuring fairness. They must be statutory, pertain to judicial decrees, and involve aggrieved parties.

lex-o-pedia
What is Greenwashing? Why Do Sustainability Claims Need Regulation and Transparency?
Greenwashing misleads consumers with false eco-friendly claims, harming both trust and real sustainability. High-profile cases show why clear regulations and transparency are crucial for accountability.

lex-o-pedia
Who is a Muslim, and what are the key sources of Muslim law?
Muslim law in India stems from the Quran, Hadith, Ijma, and Qiyas. These primary sources, along with legislation, judicial decisions, and customs, create a balanced yet adaptable legal framework for Muslims.
lex-o-pedia
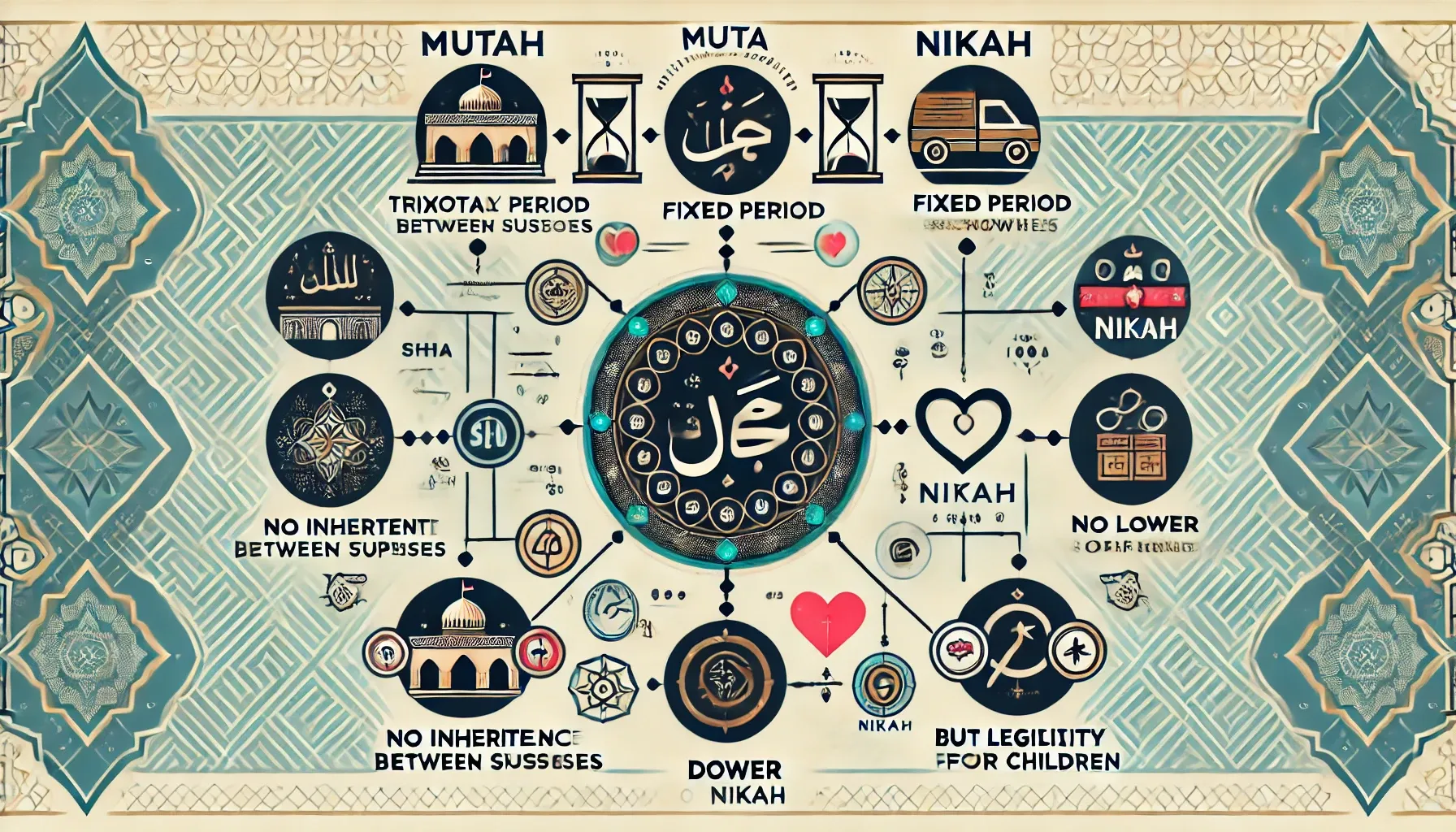
What is Muta Marriage?
Muta marriage, a temporary union in Shia law, sets a defined period and dower. While it provides legitimacy to children, it lacks mutual inheritance rights and maintenance unless specified in the agreement.

lex-o-pedia
What is the art of drafting pleadings, and how can it contribute to effective civil litigation?
Pleadings are written statements in civil cases outlining facts, claims, and defenses. They help clarify issues, guide the court, and ensure transparency, forming the basis for an organized and fair trial.

lex-o-pedia
What is parentage and legitimacy under Muslim law?
Under Muslim law, parentage defines legal rights for children, focusing on legitimacy established through lawful marriage. Maternity is clear-cut, while paternity and legitimacy hinge on valid wedlock.

lex-o-pedia
How are the constitution, procedure, and objectives of the Central Consumer Protection Council defined?
The Central Consumer Protection Council (CCPC) in India safeguards consumer rights, promotes fair practices, and advises on policies. It fosters consumer safety, education, and ethical business practices nationwide.
lex-o-pedia
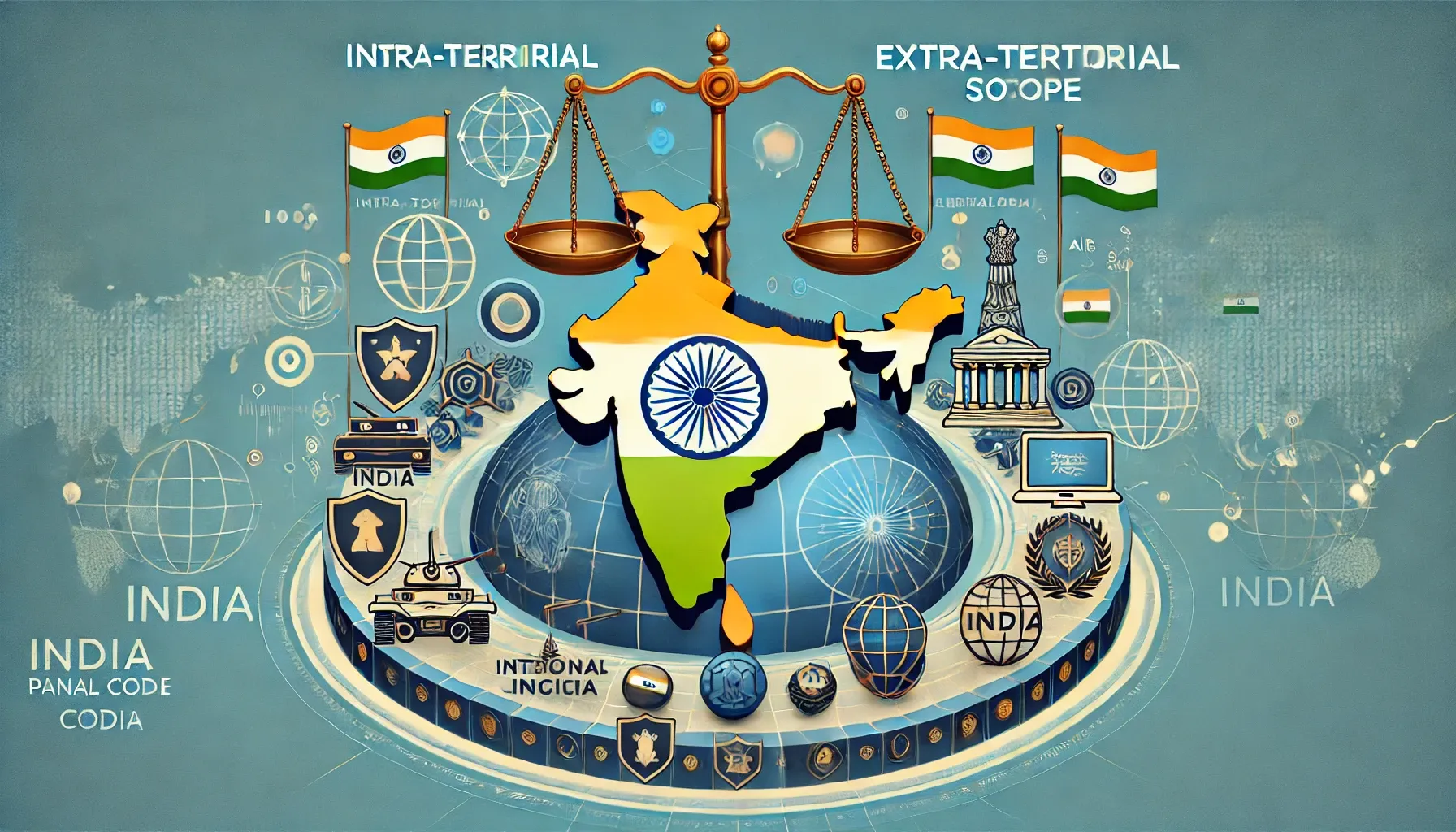
What is the difference between intra-territorial and extra-territorial jurisdiction of Indian criminal law?
This article analyzes intra-territorial and extra-territorial jurisdiction under the Indian Penal Code, detailing their definitions, applications, differences, and recent changes in the Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita 2023.
lex-o-pedia
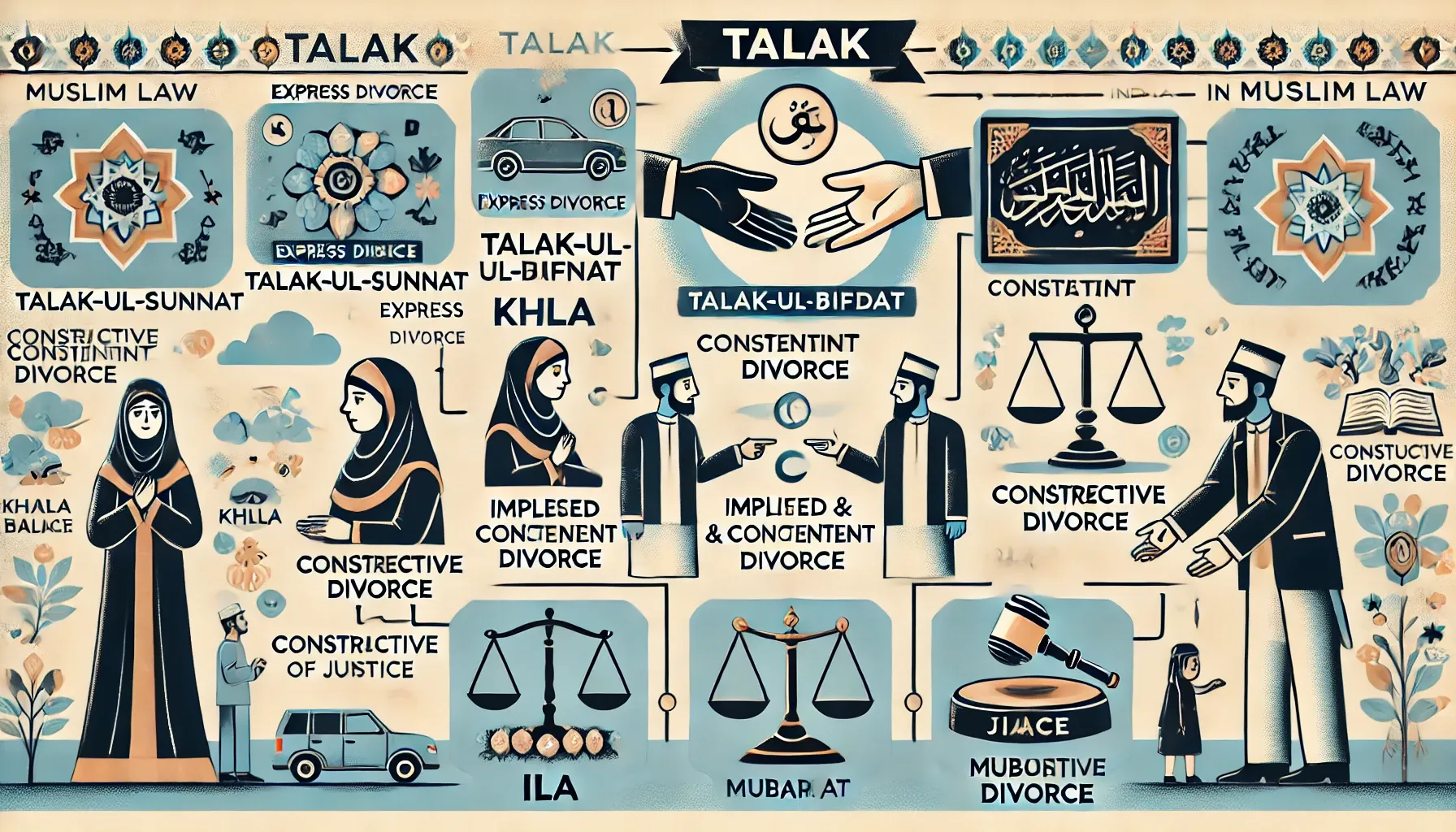
What are types of Divorce under Muslim Law?
Talak in Muslim law includes express, implied, delegated, constructive, Khula, Mubara'at, and judicial divorce, offering various grounds and processes for dissolution.

lex-o-pedia
What are Moral Rights under Copyright Law?
Moral rights in copyright law, rooted in French “droit moral,” ensure that authors retain rights to protect the integrity and authorship of their work beyond economic rights, as highlighted in the Indian Copyright Act, 1957 (Section 57). Indian law aligns with international standards, including the

lex-o-pedia
What is Idea-Expression dichotomy under copyright law?
The idea-expression dichotomy in copyright law protects only the specific expression of an idea, not the idea itself. This balance, upheld in cases like Baker v. Selden, fosters creativity by allowing creators to safeguard their work without monopolizing concepts.

