Legal Wires

lex-o-pedia
Are Government Companies considered a ‘State’ under Constitutional Law?
Government companies, often termed as "State" under Article 12 of the Indian Constitution, are subject to judicial review based on government control, public function, and alignment with state interests.
Featured Articles
buzz
buzz

buzz
Madhya Pradesh HC Orders Immediate Halt on Temple Constructions in Police Stations
The Madhya Pradesh High Court has paused temple constructions in police station premises, citing concerns over public space usage and secularism. The court issued notices to state officials, awaiting detailed orders.

buzz
20-Year-Old Conviction Overturned: High Court Says Domestic Tensions Aren’t Always Legal Cruelty
The Bombay High Court quashed a 20-year-old conviction for cruelty under IPC 498A, stating the allegations, like taunting and restricting movements, were insufficient to prove physical or mental cruelty.

buzz
Supreme Court Affirms AMU's Minority Rights Despite National Importance Status
The Supreme Court affirmed that Aligarh Muslim University retains its minority status despite its designation as an institution of National Importance, emphasizing that both attributes can coexist.

buzz
Swiggy and Zomato Found in Breach of Antitrust Laws, CCI Investigation Reveals Exclusive Contracts
The CCI probe finds Swiggy and Zomato engaged in exclusive contracts with restaurants, hindering market competition. The investigation follows a 2022 complaint by the National Restaurant Association of India.

buzz
High Court Disposes Plea on The Satanic Verses Import Ban, Missing Notification Raises Legal Questions
The Delhi HC disposed of a plea challenging a 1988 import ban on The Satanic Verses, citing that the notification could not be located by authorities, presuming it nonexistent for further legal actions.

buzz
Supreme Court Ends Jet Airways Revival Hopes, Orders Liquidation Amidst NCLAT Judgment Dispute
The Supreme Court ordered Jet Airways' liquidation, criticizing the NCLAT's decision to approve the Jalan-Kalrock Consortium takeover despite unmet financial commitments necessary for the airline's revival.

buzz
7:2 Supreme Court Ruling: Supreme Court Refines Scope of Article 39(b), Limits State's Power Over Private Property
The Supreme Court's 7:2 ruling clarifies that not all private property falls under "material resources of the community" in Article 39(b), protecting certain private rights while allowing specific resources for public welfare.

buzz
Karnataka HC Hears Plea to Transfer MUDA Scam Case to CBI, Questions Public Confidence in Lokayukta Investigation
The Karnataka High Court has requested Chief Minister Siddaramaiah’s response on a plea to transfer the MUDA scam investigation from Lokayukta to CBI, emphasizing public confidence in transparency.

buzz
Supreme Court Upholds UP Madarsa Act, Overturns Allahabad HC Ruling, Rules It Does Not Violate Secularism
On Nov 5, the Supreme Court upheld the UP Madarsa Education Act, overturning the Allahabad HC’s ruling on secularism grounds but struck down provisions conflicting with the UGC Act, affirming minority education rights.
case-study
case-study

case-study
Case Study: Rustom Cavasjee Cooper and Ors. v. Union of India
In Rustom Cavasjee Cooper v. Union of India, the Supreme Court invalidated the 1969 bank nationalization act, citing inadequate compensation and violation of property rights, thus breaching Articles 14, 19, and 31.

case-study
Case Study: Sajjan Singh v. State of Rajasthan
The Supreme Court in Sajjan Singh v. State of Rajasthan upheld the 17th Constitutional Amendment, validating its addition of laws to the Ninth Schedule, aimed at supporting socio-economic land reforms.

case-study
Case Study: Sulochana Amma v. Narayanan Nair
In Sulochana Amma v. Narayanan Nair (1994), the Supreme Court upheld the application of res judicata to injunction decrees from courts with limited pecuniary jurisdiction. The case involved property rights and multiple suits following the alienation of a life estate. The Court ruled that once a comp

case-study
Case Study: Nanchand Gangaram v. Malappa Mahalingappa
In Nanchand Gangaram v. Malappa Mahalingappa (AIR 1976 SC 835), the Supreme Court held that Section 45 of the Indian Partnership Act does not apply to Hindu Joint Families, as these are based on status, not contract. The court emphasized that a Karta’s acknowledgment of debt cannot extend the statut

case-study
Case Study: Gherulal Parakh v. Mahadeodas Maiya
In Gherulal Parakh v. Mahadeodas Maiya (AIR 1959 SC 781), the Supreme Court of India held that while wagering contracts are void under Section 30 of the Indian Contract Act, they are not illegal under Section 23. The court ruled that partnerships formed for wagering purposes are not unlawful, as wag

case-study
Case Study: Y. Narasimha Rao and Ors v. Y. Venkata Lakshmi and Ors
In Y. Narasimha Rao and Ors v. Y. Venkata Lakshmi and Ors (1991), the Supreme Court of India ruled that a foreign court’s decree dissolving a marriage is unenforceable if it lacks jurisdiction under Indian law. The Missouri court’s divorce decree, based on “irretrievable breakdown of marriage,” was

case-study
Case Study: Balvant N. Viswamitra and Ors. v. Yadav Sadashiv Mule (Dead) through Lrs. and Ors.
In Balvant N. Viswamitra and Ors. v. Yadav Sadashiv Mule (Dead) through Lrs. and Ors., the Supreme Court of India held that a decree passed by a court of competent jurisdiction is not void, even if erroneous, unless the court lacks jurisdiction over the subject matter or the parties. The High Court’

case-study
Case Study: Addanki Narayanappa and Ors. v. Bhaskara Krishtappa and Ors.
In Addanki Narayanappa and Ors. v. Bhaskara Krishtappa and Ors. (1966), the Supreme Court of India clarified that a partner’s interest in a firm during its existence is not specific to any particular asset, whether movable or immovable. Partners have no claim over specific properties but only to a s

case-study
Case Study: Satya v. Teja Singh
“Indian courts are not bound to recognize foreign divorce decrees
columns
columns
columns
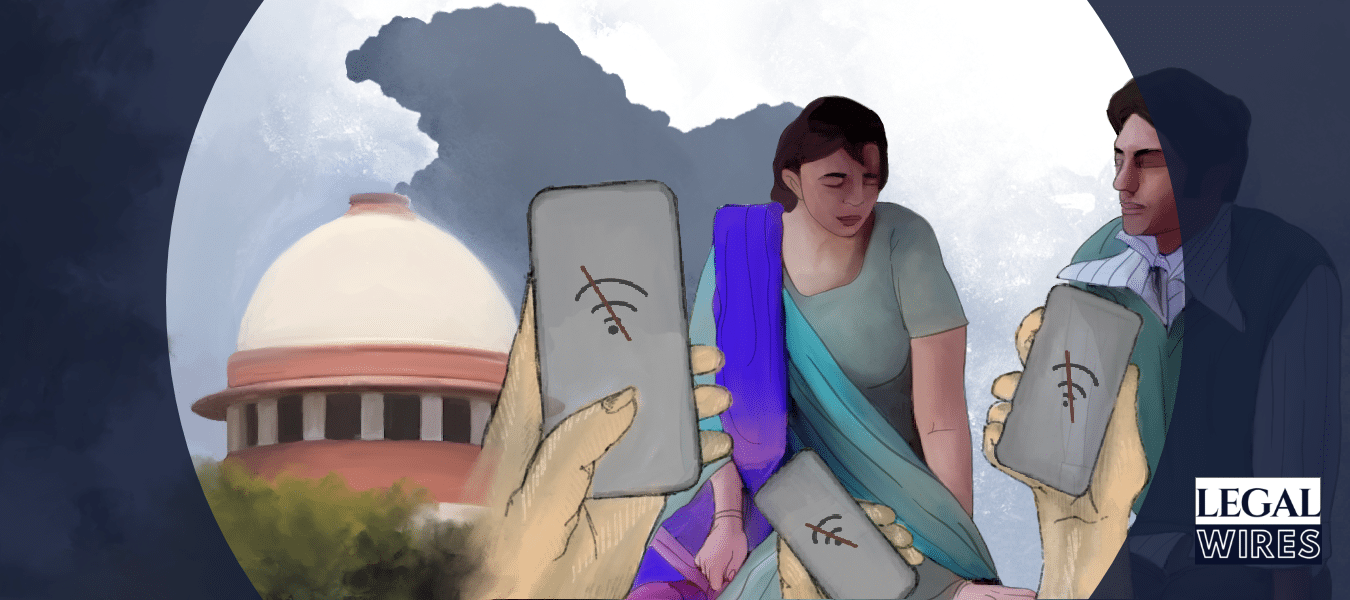
Understanding Anuradha Bhasin v. Union of India: The Kashmir Internet Shut-down case
This case also boiled around to discover as to what is more important, liberty or security? And to strike a balance between liberty and security issues to an extent that fundamental rights are secured and enjoyed in the most appropriate way.

columns
नंगे राष्ट्र का कानून
– बेरहम देश में महिलाओ के खिलाफ अपराध बहुत बढ़

columns
Australia passes the Draconian ‘Surveillance Bill’
The post-Internet age has seen a clash between the Privacy
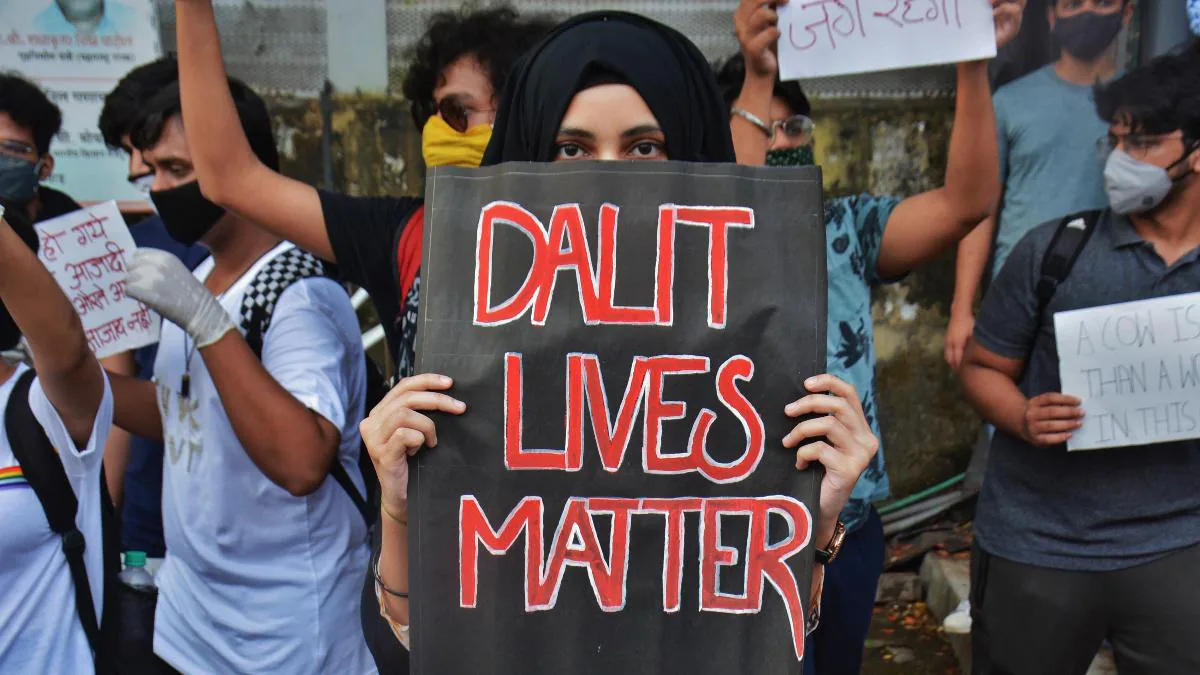
columns
Dalit Horrors Remembrance Day: Commemorating the weeks into 75th Independence Day
Vandana Katariya.
The Indian prodigy, who was India’s top goal scorer in 2013 Junior World Cup. The Hockey India’s Player of the Year 2014. Got us Silver at Asian Champion Trophy 2018, and becoming the Player of the Tournament Award.

columns
Principle of Non-Retroactivity of Penal Statues: A Fundamental Human Right?
Introduction The deep-rooted antipathy towards retrospective laws is an ancient

columns
Making Sense of the RTI and its 2019 Amendment: A paradigm for ‘Swarth Rajya’
This right is not expressly mentioned in the Indian Constitution but can be derived from Article 19 and 21 respectively.
columns
Advocates (Amendment) Bill, 2017: Parody or Necessity?
INTRODUCTION Since Independence and even before that, advocates held a

columns
Khaki Mafia: Torture, Impunity and Indolence
The National Campaign Against Torture (NCAT) in its “India: Annual Report on Torture 2019” reported that a total of 1,731 persons died in custody during 2019, i.e. death of about five persons daily.[13] Out of which 1,606 deaths were reported in judicial custody and 125 deaths in police custody.

columns
Dr. Ambedkar on Marxist Idea of Religion
– Shivani Chauhan, Mohammad Adil Ansari Introduction When we look
glossary
glossary

glossary
Legal Maxim: De minimis non curat lex
“De minimis non curat lex,” a Latin maxim meaning “The law does not concern itself with trifles,” signifies that courts should not waste time on minor, insignificant matters. Originating from Roman law, this principle is reflected in Section 95 of the Indian Penal Code, which prevents penalizing tri

glossary
Legal Maxim: Suppressio Veri or Suggestio Falsi
The legal maxim “suppressio veri or suggestio falsi” signifies that the suppression of truth is equivalent to the suggestion of falsehood. This principle holds that if either the omission of relevant facts or the presentation of false information regarding a material fact in a contract can be proven

glossary
Legal Maxim: Noscitur a Sociis
The legal maxim “Noscitur a Sociis” means “it is known by its associates.” This doctrine asserts that the meaning of an unclear word in a statute or contract should be determined by the words surrounding it. It emphasizes context, ensuring the interpretation aligns with the document’s overall intent

glossary
Glossary: Nemo Debet Esse Judex In Propria Sua Causa
“Nemo debet esse judex in propria sua causa” is a Latin legal maxim meaning “no one should be a judge in their own cause.” This principle ensures fairness and impartiality in legal proceedings by preventing conflicts of interest. It upholds the integrity of the judicial system by guaranteeing that d

glossary
Glossary: Allegans Contraria Non Est Audiendus
“Allegans contraria non est audiendus,” a Latin legal maxim, translates to “a person alleging contradictory facts is not to be heard.” This principle emphasizes consistency in legal arguments, asserting that one cannot present conflicting statements or claims within the same case. It is fundamental

glossary
Vakalatnama
A Vakalatnama is a legal document authorizing an advocate to represent a client in a court of law. It grants the lawyer the power to act on behalf of the client, including filing suits, attending hearings, and signing pleadings. Typically, the client signs the Vakalatnama, and it is submitted to the

glossary
Legal Maxim: Actori Incumbit Onus Probandi
Actori Incumbit Onus Probandi, a Latin legal maxim, means “the burden of proof lies on the plaintiff.” The burden of proof requires the plaintiff to establish the facts of the case to the requisite standard of proof, typically “beyond a reasonable doubt” in criminal cases and “preponderance of evide
glossary
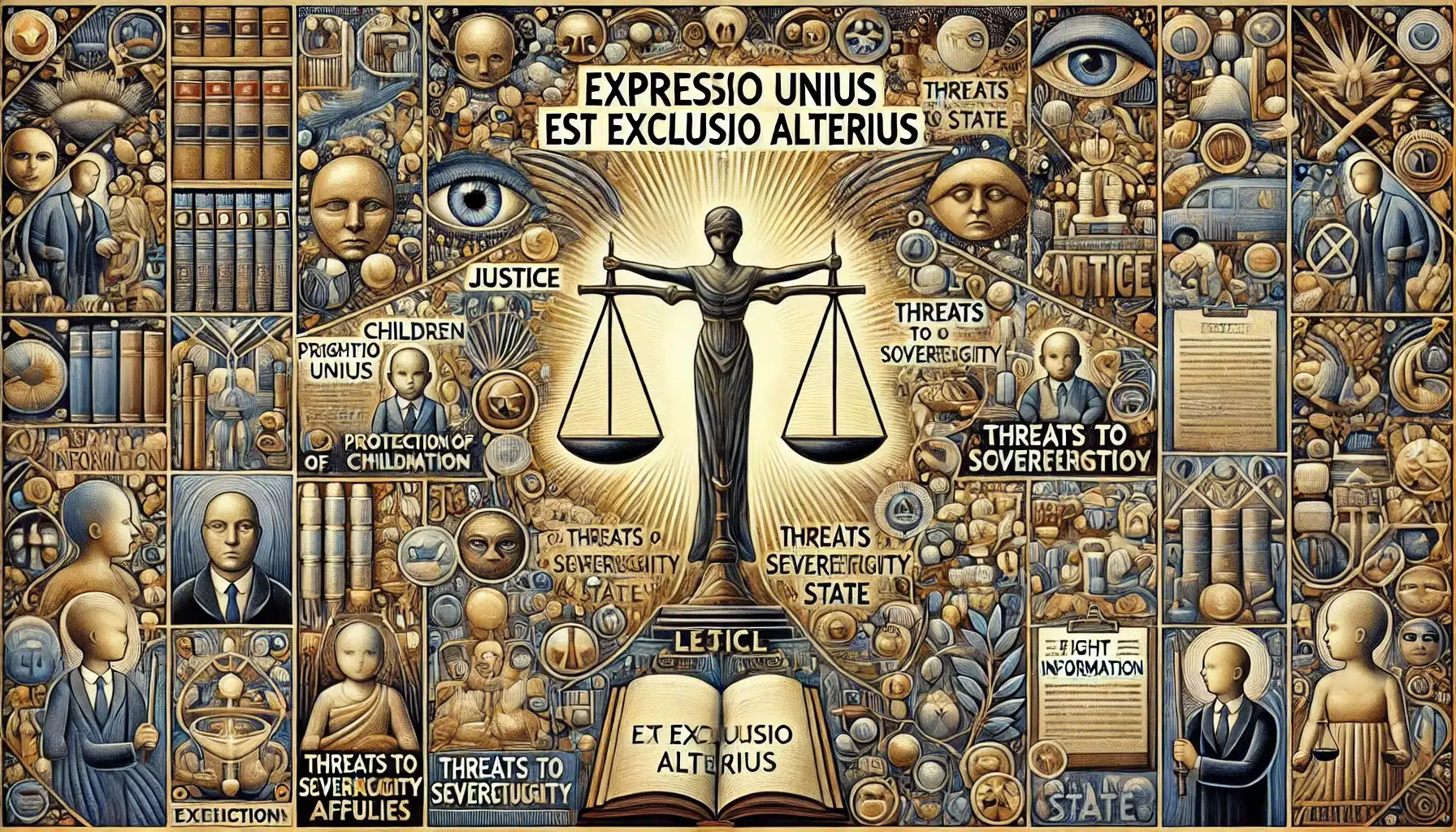
Legal Maxim: Expressio Unius Est Exclusio Alterius
xpressio Unius Est Exclusio Alterius is a legal maxim meaning “the expression of one thing is the exclusion of another.” It is used in statutory interpretation to infer that if a law explicitly mentions certain items, other items not mentioned are excluded.

glossary
Glossary: Volenti Non Fit Injuria
Volenti non fit injuria is a latin maxim which means “to a willing person, it’s not a wrong”. It implies that if someone willingly puts themselves in a position where harm might occur, they cannot later sue for any resulting damages. This doctrine is often used as a defence in personal injury cases
lex-o-pedia
lex-o-pedia

lex-o-pedia
Are Government Companies considered a ‘State’ under Constitutional Law?
Government companies, often termed as "State" under Article 12 of the Indian Constitution, are subject to judicial review based on government control, public function, and alignment with state interests.

lex-o-pedia
What is the Concept and Process of Appeal in the Code of Civil Procedure (CPC)?
Appeals in the Indian Code of Civil Procedure enable dissatisfied parties to seek higher court review of lower court judgments, ensuring fairness. They must be statutory, pertain to judicial decrees, and involve aggrieved parties.

lex-o-pedia
What is Greenwashing? Why Do Sustainability Claims Need Regulation and Transparency?
Greenwashing misleads consumers with false eco-friendly claims, harming both trust and real sustainability. High-profile cases show why clear regulations and transparency are crucial for accountability.

lex-o-pedia
Who is a Muslim, and what are the key sources of Muslim law?
Muslim law in India stems from the Quran, Hadith, Ijma, and Qiyas. These primary sources, along with legislation, judicial decisions, and customs, create a balanced yet adaptable legal framework for Muslims.
lex-o-pedia
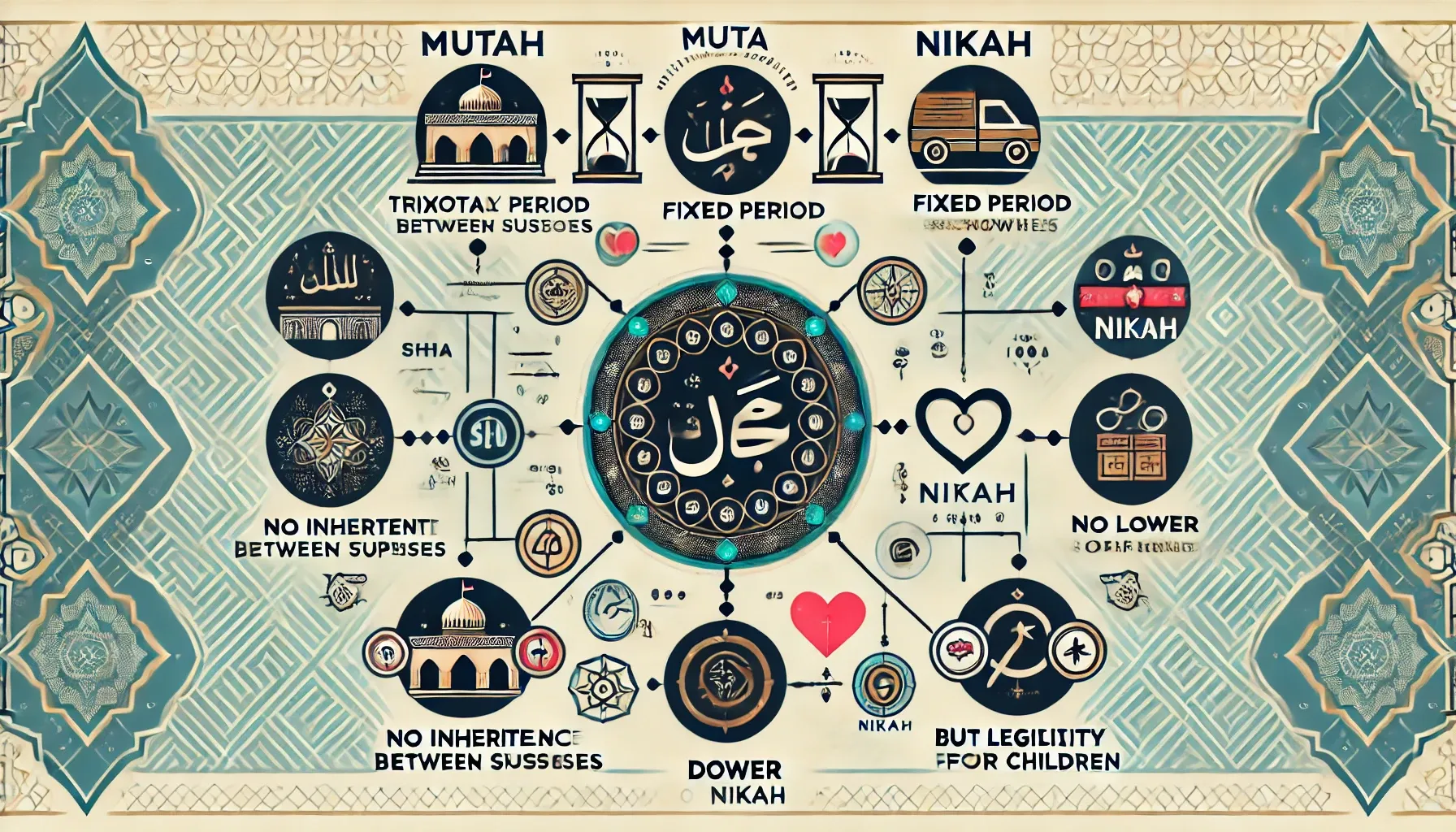
What is Muta Marriage?
Muta marriage, a temporary union in Shia law, sets a defined period and dower. While it provides legitimacy to children, it lacks mutual inheritance rights and maintenance unless specified in the agreement.

lex-o-pedia
What is the art of drafting pleadings, and how can it contribute to effective civil litigation?
Pleadings are written statements in civil cases outlining facts, claims, and defenses. They help clarify issues, guide the court, and ensure transparency, forming the basis for an organized and fair trial.

lex-o-pedia
What is parentage and legitimacy under Muslim law?
Under Muslim law, parentage defines legal rights for children, focusing on legitimacy established through lawful marriage. Maternity is clear-cut, while paternity and legitimacy hinge on valid wedlock.

lex-o-pedia
How are the constitution, procedure, and objectives of the Central Consumer Protection Council defined?
The Central Consumer Protection Council (CCPC) in India safeguards consumer rights, promotes fair practices, and advises on policies. It fosters consumer safety, education, and ethical business practices nationwide.
lex-o-pedia
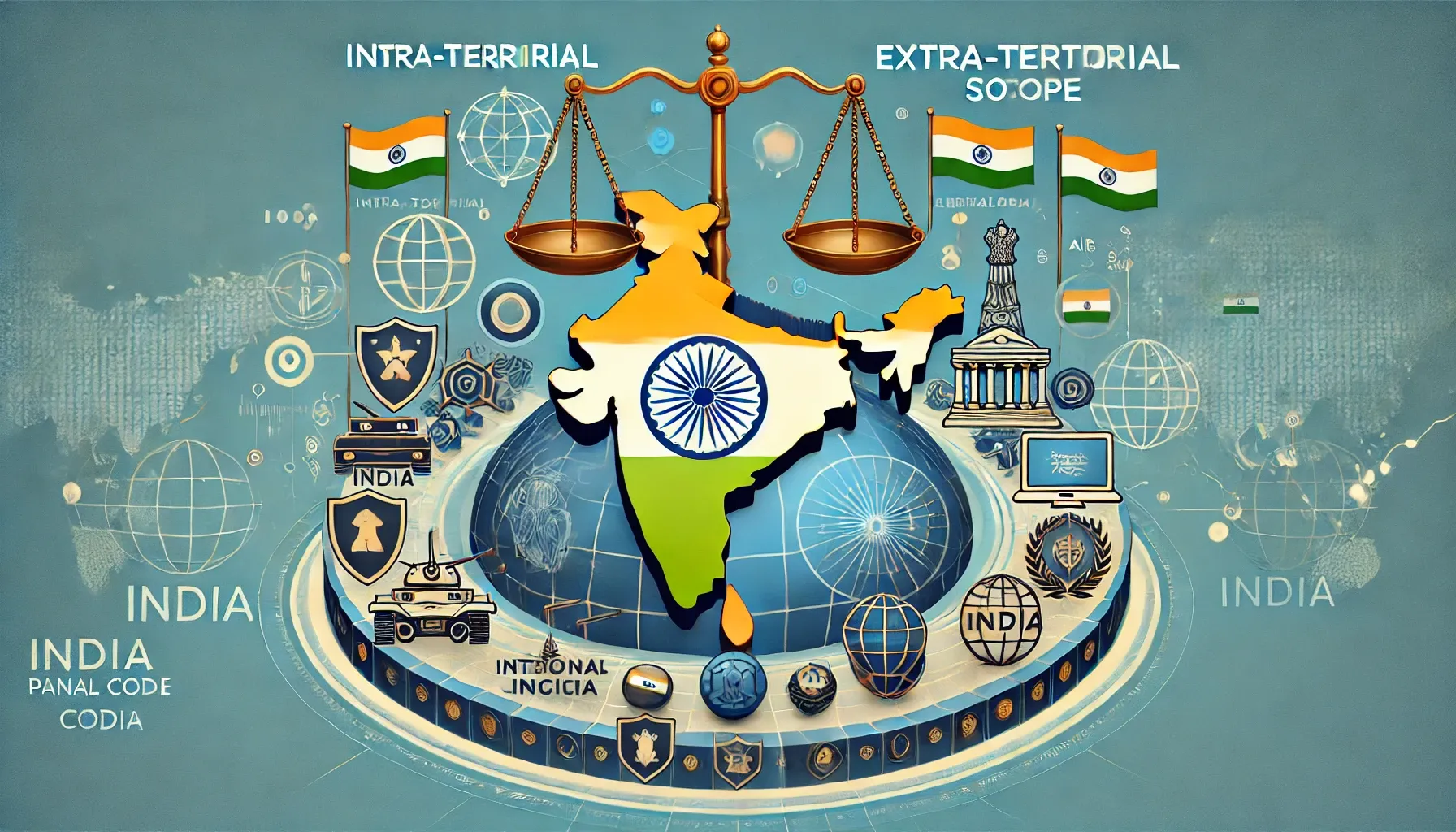
What is the difference between intra-territorial and extra-territorial jurisdiction of Indian criminal law?
This article analyzes intra-territorial and extra-territorial jurisdiction under the Indian Penal Code, detailing their definitions, applications, differences, and recent changes in the Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita 2023.